
You can also pulse the motor control line, (A or B) on and off. If you hook up these circuits you can only get the motor to stop or turn in one direction, forward for the first circuit or reverse for the second circuit. Apply a logical zero, which is usually a ground, causes the motor to stop spinning. Hook the motor up in this fashion and the circuit turns the motor in reverse when you apply a logical one (+12Volts) to point B. Applying a logical zero, (ground) causes the motor to stop turning (to coast and stop). If you connect this circuit to a small hobby motor you can control the motor with a processor (MCU, etc.) Applying a logical one, (+12 Volts in our example) to point A causes the motor to turn forward. The bar, which is the Cathode side of the diode, should connect to the coil where the MCU connects to the relay. The anode, which is the arrow side of the diode, should connect to ground. This will keep the spike voltage (back EMF), coming out of the coil of the relay, from getting into the MCU and damaging it. NOTE: If you connect up these relay circuits, remember to put a diode across the coil of the relay. Now lets say you want a Micro Controller Unit (MCU) to control the motor, how would you do it? Well, for starters you get a device that would act like a solid state switch, a transistor, and hook it up the motor.

If you swap the battery leads the motor spins in reverse. Then you connect the negative side of the battery to the other motor lead. You take a battery hook the positive side to one side of your DC motor.
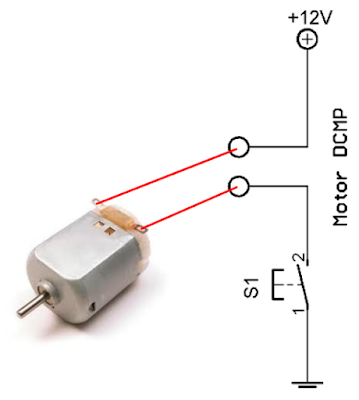

What’s all this talk about H-Bridges? How do they work? Well let’s see. September 2002, page format revised, links updated by Bob Jordan


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
